Table of Contents
sdSuSiE is a package designed for sex-dimorphic fine-mapping using summary statistics from sex-stratified genome-wide association studies (GWAS). This package includes:
- A Bayesian method: sdSuSiE, which explicitly models sex differences in genetic effects while accounting for correlations induced by linkage disequilibrium and sample size imbalances between sexes. It uses summary statistics from sex-stratified GWASs as inputs and extends the recent scalable variational inference algorithm SuSiE to fine-map sex-dimorphic effects.
- A frequentist method: stepwise regression, which extends the standard stepwise selection procedure in the COJO framework for sex-dimorphic fine-mapping.
Commonly used sex-stratified GWAS summary statistics can be obtained from:
- Neale Lab UK Biobank GWAS results
- Global Lipids Genetics Consortium (GLGC) Results
- GIANT Consortium Results
This tutorial demonstrates an example analysis of a genomic region spanning 64,203,593 to 65,203,593 on chromosome 14 for haemoglobin concentration using included data.
Installation #
devtools::install_github('yuanzhongshang/sdSuSiE')
library(sdSuSiE)
Ensure successful installation before proceeding. For detailed installation instructions, see the installation guide.
Loading the necessary data #
The package comes with the necessary data included. These data included the summary statistics for male-only and female-only GWASs, and their corrosponding LD matrices. Each GWAS summary statistics dataset must contain columns named SNP, Beta, Se, Z, and N, which correspond to the SNP information, marginal effect size, standard error, Z-score, and sample size, respectively.
data(GWAS_M)
data(GWAS_F)
data(LD_M)
data(LD_F)
# Male-only GWAS data
head(GWAS_M)
SNP Beta Se Z N POS
1 rs77016686 0.00727264 0.00869551 0.836367 162398 64203861
2 rs8013824 -0.00108723 0.00940082 -0.115653 162398 64204482
3 rs112382458 -0.00879382 0.00586182 -1.500190 162398 64205218
4 rs115468696 0.00760802 0.00865580 0.878950 162398 64205807
5 rs61985698 -0.02698580 0.01594060 -1.692900 162398 64205915
6 rs189077474 -0.06524800 0.04598900 -1.418780 162398 64206396
# Female-only GWAS data
head(GWAS_F)
SNP Beta Se Z N POS
1 rs77016686 -0.000731382 0.00806516 -0.0906842 188076 64203861
2 rs8013824 -0.014274300 0.00863349 -1.6533600 188076 64204482
3 rs112382458 0.000795164 0.00541292 0.1469010 188076 64205218
4 rs115468696 -0.000631569 0.00802782 -0.0786725 188076 64205807
5 rs61985698 -0.014655600 0.01454600 -1.0075300 188076 64205915
6 rs189077474 -0.092397400 0.04546230 -2.0323900 188076 64206396
# Male LD matrix
LD_M[1:5,1:5]
rs77016686 rs8013824 rs112382458 rs115468696 rs61985698
rs77016686 1.00000000 -0.04073675 -0.06163991 0.99344917 -0.02004854
rs8013824 -0.04073675 1.00000000 -0.06673863 -0.04096559 -0.01808016
rs112382458 -0.06163991 -0.06673863 1.00000000 -0.06155264 -0.03163928
rs115468696 0.99344917 -0.04096559 -0.06155264 1.00000000 -0.01984281
rs61985698 -0.02004854 -0.01808016 -0.03163928 -0.01984281 1.00000000
# Female LD matrix
LD_F[1:5,1:5]
rs77016686 rs8013824 rs112382458 rs115468696 rs61985698
rs77016686 1.00000000 -0.03821470 -0.06592288 0.99527431 -0.01910618
rs8013824 -0.03821470 1.00000000 -0.06662310 -0.03896861 -0.01825061
rs112382458 -0.06592288 -0.06662310 1.00000000 -0.06634842 -0.02993899
rs115468696 0.99527431 -0.03896861 -0.06634842 1.00000000 -0.01987188
rs61985698 -0.01910618 -0.01825061 -0.02993899 -0.01987188 1.00000000
Run sdSuSiE #
To use sdSuSiE, two lists are required: one for summary statistics and another for LD matrices, each from males and females. It’s essential to name each element in these lists, ensuring that the naming is consistent between the summary statistics and LD matrices.
summary_list = list()
summary_list[[1]] = GWAS_M
summary_list[[2]] = GWAS_F
names(summary_list) = c("Male","Female")
LDmat_list = list()
LDmat_list[[1]] = LD_M
LDmat_list[[2]] = LD_F
names(LDmat_list) = c("Male","Female")
res = sdSuSiE(LDmat_list, summary_list)
*************************************************************
Sex-dimorphic mapping with sum of the single effects model (sdSuSiE)
Visit https://xiangzhou.github.io/software/ For Update
(C) 2025 Lu Liu, Xiang Zhou
GNU General Public License
*************************************************************
# Start data processing for sufficient statistics
# Create sdSuSiE object
# Start data analysis
# Data analysis is done, and now generates result
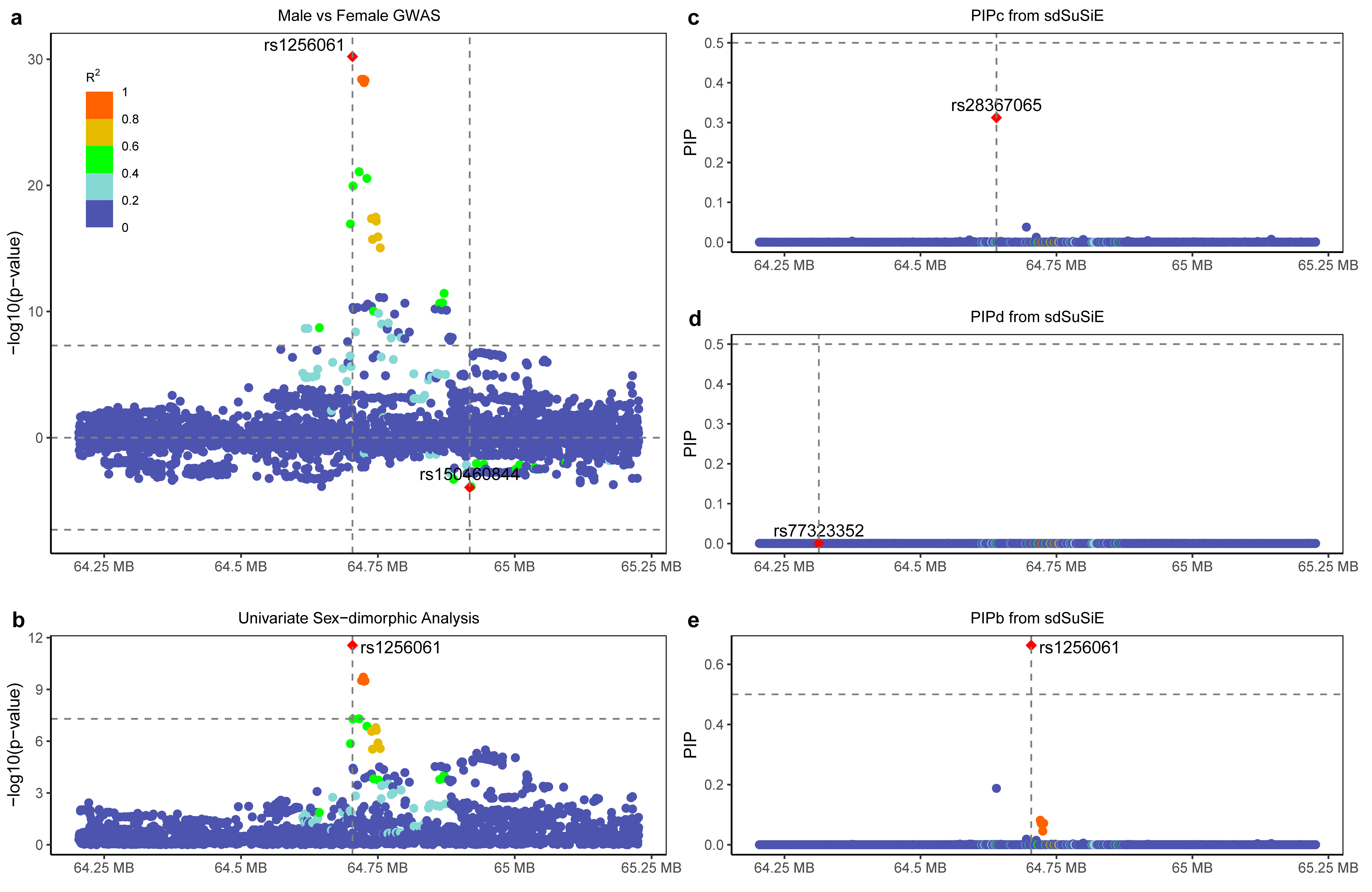
Potential causal SNPs with common effect (PIPc > 0.5):
Potential causal SNPs with sex-dimorphic effect (PIPd > 0.5):
Potential causal SNPs with both common and sex-dimorphic effects (PIPb > 0.5): rs1256061
Credible sets for effects:
$cs
$cs$L1
[1] 1099 1120 1128 1132 1138
$cs_category
L1
"Both"
$purity
min.abs.corr mean.abs.corr median.abs.corr
L1 0.9253243 0.9749922 0.9964113
$cs_index
[1] 1
$coverage
[1] 0.9547394
$requested_coverage
[1] 0.95
Use sdSuSiE_Plot() for visualization
# Total time used for the analysis: 0.51 mins
Below are the optional inputs:
- L: The maximum number of non-zero effects assumed within the region (default:
10). - residual_variance: A numeric vector (default:
c(1, 1)) specifying the residual variance for males and females. - prior_weights: A numeric vector of length p specifying the prior probability that each SNP has a non-zero effect. By default, prior weights are assumed to be equal for all SNPs.
- config_weights: A numeric vector of length 3 specifying the prior probabilities for different causal configurations: The first element represents the probability of a SNP having a common effect. The second element represents the probability of a SNP having a sex-dimorphic effect. The third element represents the probability of a SNP having both common and sex-dimorphic effects. The three elements must sum to 1. The default prior values are
-1 + sqrt(2),-1 + sqrt(2), and(-1 + sqrt(2))^2, respectively. - config_names: A character vector of length 3 specifying the names for different causal configurations. The default prior values are
Common,Sex-dimorphic, andBoth, respectively. - estimate_residual_variance: A logical value indicating whether the residual variance should be estimated (TRUE) or fixed (
FALSE, default). - cor_method: A string specifying the method to compute the 95% credible set based on correlations among SNPs in the region. Options include:
"min_abs_corr": Minimum absolute correlation (default); “mean_abs_corr”: Mean absolute correlation; “median_abs_corr”: Median absolute correlation.
The output is an R6 object with PIPs, credible sets, and other features of the sex-dimorphic fine-mapping result.
head(res$PIP_config)
Common Sex-dimorphic Both
[1,] 1.442247e-04 0.0001582806 4.632963e-05
[2,] 3.559284e-04 0.0001501440 1.485142e-04
[3,] 9.773441e-05 0.0001314281 3.933884e-05
[4,] 1.480176e-04 0.0001589961 4.670208e-05
[5,] 2.142240e-04 0.0001597608 8.070750e-05
[6,] 1.868119e-04 0.0001665844 8.010555e-05
res$Credible_Set
$cs
$cs$L1
[1] 1099 1120 1128 1132 1138
$cs_category
L1
"Both"
$purity
min.abs.corr mean.abs.corr median.abs.corr
L1 0.9253243 0.9749922 0.9964113
$cs_index
[1] 1
$coverage
[1] 0.9547394
$requested_coverage
[1] 0.95
head(res$posterior_mean)
beta_c beta_d
[1,] 4.948462e-06 -1.359433e-06
[2,] -3.038267e-05 -4.130769e-06
[3,] 2.053571e-06 9.146973e-07
[4,] 5.335527e-06 -1.400183e-06
[5,] -1.465196e-05 -1.108200e-06
[6,] -1.108672e-05 -1.291108e-06
head(res$posterior_variance)
var_c var_d var_cd
1 3.237029e-08 1.307772e-08 2.928244e-09
2 9.564001e-08 1.621912e-08 1.030286e-08
3 1.236151e-08 8.005936e-09 1.364242e-09
4 3.301176e-08 1.311215e-08 2.936075e-09
5 1.003058e-07 1.894693e-08 9.375536e-09
6 1.702456e-07 2.360243e-08 1.234180e-08
The main results we are interested in include:
- PIP: A vector where each element represents the PIP of a SNP having a non-zero effect.
- PIP_config: A matrix where each column corresponds to the PIP of a causal configuration. The columns represent the PIP of a SNP having a common effect, a sex-dimorphic effect, or both.
- alpha: A list of length L, where each element is a matrix (p by the number of causal configurations) of PIPs. Each column represents the PIP for a causal configuration.
- KL: A vector containing the single-effect Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergences.
- sigma2: A numeric vector of estimated residual variance.
- V: A list of length L, where each element is a 2 by 2 matrix representing the prior variance estimate.
- ELBO: A vector storing the evidence lower bound (ELBO) achieved at each iteration of the model-fitting algorithm, which aims to maximize the ELBO.
- Credible_Set: The estimated credible sets for fine-mapping.
- posterior_mean: A matrix where the first column contains the posterior mean for βc (common effects) and the second column contains the posterior mean for βd (sex-dimorphic effects).
- posterior_variance: A matrix with the first column being the variance for βc, the second column being the variance for βd, and the third column being the covariance between βc and βd.
The result can be visualized with the sex-stratified GWASs, univariate sex-dimorphic analysis and sdSuSiE results in Locuszoom plots.
sdSuSiE_Plot(res, LDmat_list, summary_list)
Run stepwise regression #
To use stepwise regression, one data frame containing summary statistics of univariate common effects and sex-dimorphic effects, and their corresponding LD matrix are required. It’s essential to ensure that the naming is consistent between the summary statistics and LD matrices. The data frame must contain columns named SNP, Beta, Se, Z, N, and p, which correspond to the SNP information, univariate effect size, standard error, Z-score, sample size, and p-value, respectively. These summary statistics can be derived using the sex-stratified GWAS summary statistics.
# Convert the sex-stratified GWAS summary statistics and LD matrices to the required format.
SNP = GWAS_M$SNP
Z = (sqrt(GWAS_M$N - 1) * GWAS_M$Z + sqrt(GWAS_F$N - 1) * GWAS_F$Z) / sqrt(GWAS_M$N + GWAS_F$N - 1)
N = round(GWAS_M$N + GWAS_F$N)
Beta = Z / sqrt(N - 1)
Se = 1 / sqrt(N - 1)
data1 = data.frame(SNP, Beta, Se, Z, N)
SNP = paste0("S*", SNP)
Z = (-sqrt(GWAS_M$N - 1) * GWAS_M$Z + sqrt(GWAS_F$N - 1) * GWAS_F$Z) / sqrt(GWAS_M$N + GWAS_F$N - 1)
N = round(GWAS_M$N + GWAS_F$N)
Beta = Z / sqrt(N - 1)
Se = 1 / sqrt(N - 1)
data2 = data.frame(SNP, Beta, Se, Z, N)
data = rbind(data1, data2)
data$p = pchisq((data$Beta/data$Se)^2, df = 1, lower.tail = FALSE)
N_M = round(median(GWAS_M$N))
N_F = round(median(GWAS_F$N))
N = N_M + N_F
V1 = (N_M-1)*LD_M + (N_F-1)*LD_F
V2 = (-1)*(N_M-1)*LD_M + (N_F-1)*LD_F
LD = rbind(cbind(V1,V2),cbind(V2,V1)) / (N-1)
res = sdstepwise(data, LD)
Below are the optional inputs:
- p_cutoff: A numeric value specifying the p-value threshold for selecting significant SNPs in the stepwise regression process (default:
5e-8). - collinear: A numeric value specifying the maximum allowable collinearity among selected SNPs (default:
0.9). - ncore: An integer specifying the number of cores to use for parallel processing (default:
10).
The output is a data frame containing information about the selected SNPs for fine-mapping.
res
SNP Beta Se Z N p
1120 rs4365213 -0.016385647 0.001689168 -9.700428 350474 3.002378e-22
3358 S*rs4365213 0.009376802 0.001689168 5.551138 350474 2.838163e-08
p_i idx SNPu b_c se_c p_c LD_r
1120 3.887184e-24 1120 rs4365213 -0.01716485 0.00169372 3.887184e-24 0.0732667
3358 3.413038e-10 3358 rs4365213 0.01063444 0.00169372 3.413038e-10 0.0000000
sig
1120 1
3358 1
The main results we are interested in include:
- b_c: The effect size estimates of selected SNPs in the jointly fitted model.
- se_c: The standard errors of the effect size estimates.
- p_c: The p-values of selected SNPs in the jointly fitted model.
- LD_r: The pairwise LD values among selected SNPs.
- sig: Indicator of significance for each SNP (1 if p_c < 5e-8, 0 otherwise).
Contact #
If you have any questions, feel free to leave messages on the github issues.