Table of Contents
GIFT is a Gene-based Integrative Fine-mapping for performing conditional TWAS analysis. GIFT examines one genomic region at a time, jointly models the GReX of all genes residing in the focal region, and carries out TWAS conditional analysis in a maximum likelihood framework. We used LD blocks defined by LDetect: hg19, hg38. For each region, we focus on protein-coding genes and long intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) that are annotated in GENCODE (release 12). The latest release can also be downloaded here. Other definitions can also be used to determine LD blocks.
Data Availability #
The commonly used eQTL summary statistics includes: genome-wide eQTL summary statistics from GEUVADIS data, cis-eQTL and trans-eQTL summary statistics from eQTLGen Consortium, and cis-eQTL mapping summary statistics for African American and European American from GENOA.
The commonly used GWAS summary statistics can be downloaded in GWAS Catalog, GWAS ATLAS, IEU Open GWAS Project, FinnGen, Biobank Japan and Neale Lab UK Biobank GWAS results.
The commonly used reference panel are 1000 Genomes project data, and UK Biobank LD reference.
Data Preparation #
Since summary statistics may be available in different formats, we provide a guideline for data preparation.
- First, ensure the same genome builds for three datasets including eQTL, GWAS, reference panel (code for lifting over genome builds).
- Second, perform quality control on each dataset, including removing strand ambiguous variants, multi-allelic variants, and SNPs with MAF below the threshold.
- Third, obtain the overlapping SNP list with alleles in the target region. If summary statistics are only available for each gene in the cis-region, combine the set of cis-SNPs for each gene and overlap them with the SNP list from the GWAS dataset and reference panel.
- Fourth, extract SNPs from the SNP list, align the reference alleles, and switch the sign of beta or z score based on the allele. Note that, missing SNPs effect on gene in the eQTL dataset will automatically imputed with zeros in the
pre_process_summaryfunction. Following these steps, you can obtain data in the format like here, and proceed to pre-process the data into GIFT input format.
Running GIFT with Summary Statistics #
We recommend performing the GIFT analysis using the summary statistic version. If you have individual-level data, please convert it into into the corresponding summary statistics. First, ensure GIFT is successfully installed. For more details, refer to the installation guide.
#devtools::install_github('yuanzhongshang/GIFT')
library(GIFT)
The essential inputs of main function GIFT_summary for conditional analysis per region are: (1) Zscores from both eQTL data (Zscore_1) and GWAS data (Zscore_2), (2) LD matrice from both eQTL data (Sigma1) and GWAS data (Sigma2) (if these two matrices are unavailable, both Sigma1 and Sigma2 are often from the same reference panel), (3) Sample sizes of eQTL data (n1) and GWAS data(n2) , (4) gene name (gene), (5) the number of cis-SNPs for each gene (pindex). There are also optional parameters of GIFT_summary, function, which can be found in the documentation.
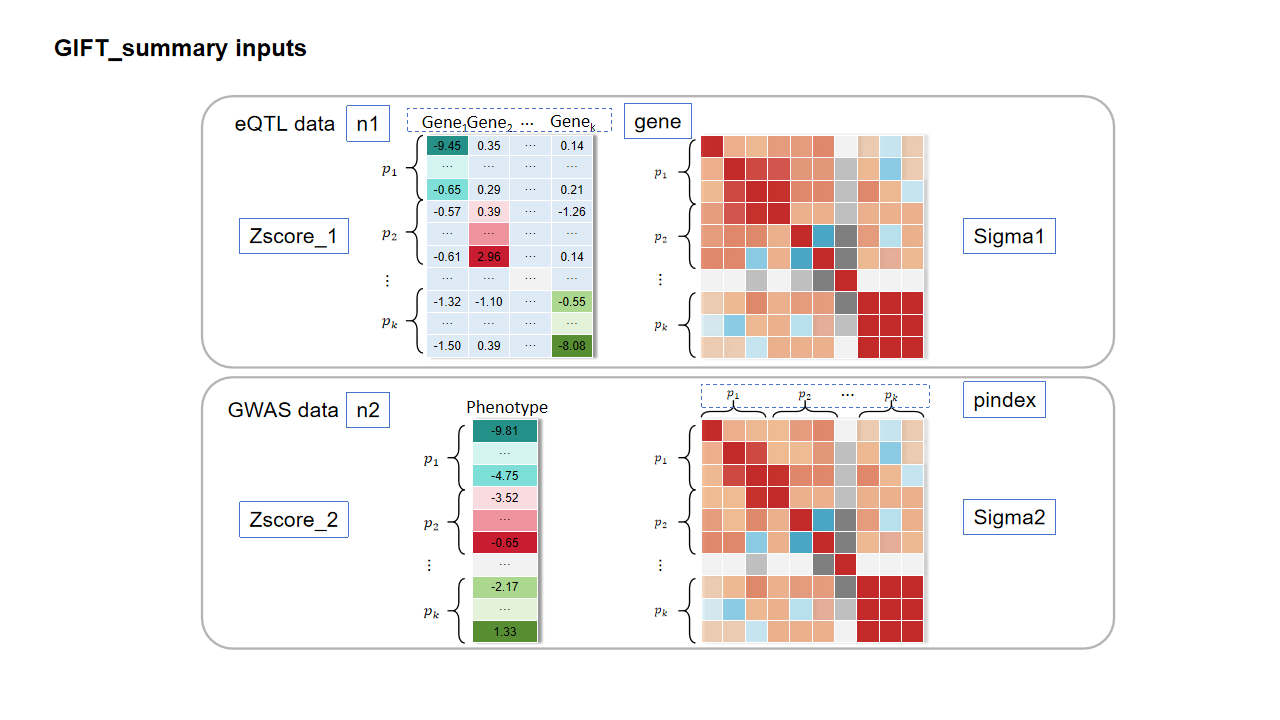
Step 1: Pre-process the summary statistics with different formats. #
In this guild, we use the simulations based on the realistic genotypes from GEUVADIS (n1=465) and UK Biobank (n2=5,000) in a region on chr 5 as an example. This region includes four genes: RASA1, COX7C, CCNH and TMEM161B. We set RASA1 as the causal gene with the effect size being sqrt(0.1). Here, we convert different summary statistics (plink (.qassoc), GEMMA (.assoc.txt) and SAIGE (.txt)) and LD matrix data formats (matrix (.txt) or h5 format (.h5)) to GIFT inputs.
library(GIFT)
dir <- getwd()
#### load the directory containing files of summary statistics from eQTL data only (e.g., the SAIGE output)
eQTLfilelocation <- paste0(dir, "/example/simulation/summary/pre_process/saige/eQTL")
#### load the directory of summary statistics from GWAS data (e.g., the SAIGE output)
GWASfile <- paste0(dir,"/example/simulation/summary/pre_process/saige/GWAS.txt")
#### load the directory of LD matrix from eQTL data and GWAS data (e.g., a long format: h5 format)
eQTLLDfile <- paste0(dir, "/example/simulation/summary/pre_process/LDmatrix1.h5")
GWASLDfile <- paste0(dir, "/example/simulation/summary/pre_process/LDmatrix2.h5")
#### load the SNP list and cis-SNP number for each gene in a region, snplist is the (p1+p2+…+pk) vector for stacked cis-SNPs of each gene.
snplist <- read.table(paste0(dir, "/example/simulation/summary/pre_process/snplist.txt"))$V1
pindex <- c(41, 23, 63, 96)
#### pre-process the file to be a list including gene names vector, z-score matrix and LD matrix of eQTL data and GWAS data
convert <- pre_process_summary(eQTLfilelocation, eQTLLDfile, GWASfile, GWASLDfile, snplist, pindex)
gene <- convert$gene
Zscore1 <- convert$Zscore1
Zscore2 <- convert$Zscore2
Sigma1 <- convert$LDmatrix1
Sigma2 <- convert$LDmatrix2
n1 <- convert$n1
n2 <- convert$n2
Step 2: Perform conditional fine-mapping for TWAS analysis. #
result <- GIFT_summary(Zscore1, Zscore2, Sigma1, Sigma2, n1, n2, gene, pindex, R=NULL, maxiter=100, tol=1e-3, pleio=0, ncores=4, in_sample_LD=T, filter=T, split=5)
The result is a data frame including the causal effect estimates and p values for each gene in a focal region.
result
gene causal_effect p
1 CCNH 0.002940875 9.712126e-01
2 COX7C 0.028515942 7.435854e-01
3 RASA1 0.364477685 1.337356e-05
4 TMEM161B -0.034292965 3.134303e-01
Note that, the summary statistics version of GIFT often requires the in-sample LD matrix. If the in-sample LD matrix is not available, it can be also calculated from the reference panel data. It would be better to ensure the ethnicity of the reference panel is consistent with that of the analyzed data, details in here. If in-sample LD was not used, the LD matrix is regularized to be (1-s1)*Sigma1+s1*E and (1-s2)*Sigma2+s2*E where both s1 and s2 are estimated by estimate_s_rss in susieR. A grid search algorithm is performed over the range from 0.1 to 1 once the estimation from susieR does not work well.
### load the LD matrix from 1,000 Genomes project
LD <- as.matrix(read.table(paste0(dir, "/example/simulation/summary/LDmatrix10000G.txt")))
result <- GIFT_summary(Zscore1, Zscore2, LD, LD, n1, n2, gene, pindex, R=NULL, maxiter=100, tol=1e-3, pleio=0, ncores=4, in_sample_LD=F, filter=T, split=5)
result
gene causal_effect p
1 CCNH 0.017590501 8.296347e-01
2 COX7C 0.007763401 8.633912e-01
3 RASA1 0.319433644 7.881041e-05
4 TMEM161B -0.064599635 3.086057e-02
Running Speed Improvement #
In the process, GIFT operates within a joint likelihood framework, accounting for the uncertainty in the constructed GReX. We acknowledge that this comprehensive approach can result in slower computational speed. Techincally, GIFT supports parallel processing for each gene using the ncores parameter. Increasing this value can significantly improve speed if your computational resources allow. On Windows, GIFT utilizes the foreach() function in combination with the “doParallel” R package. On non-Windows systems, GIFT uses mclapply() from the “parallel” R package.
Contact #
If you have any questions, feel free to leave messages on the github issues.